Abstract
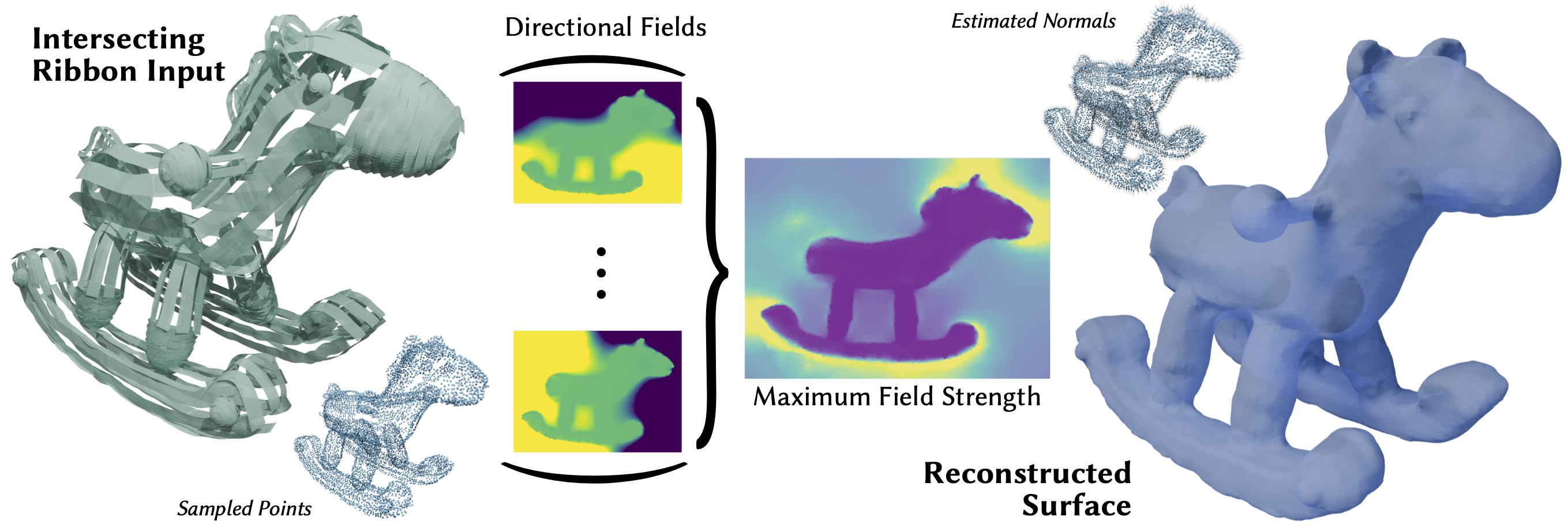
We propose a novel method (FaCE) for normal estimation of unoriented point clouds and VR ribbon sketches that leverages a modeling of the Faraday cage effect. Input points, or a sampling of the ribbons, form a conductive cage and shield the interior from external fields. The gradient of the maximum field strength over external field scenarios is used to estimate a normal at each input point or ribbon. The electrostatic effect is modeled with a simple Poisson system, accommodating intuitive user-driven sculpting via the specification of point charges and Faraday cage points. On inputs sampled from clean, watertight meshes, our method achieves comparable normal quality to existing methods tailored for this scenario. On inputs containing interior structures and artifacts, our method produces superior surfacing output when combined with Poisson Surface Reconstruction. In the case of ribbon sketches, our method accommodates sparser ribbon input while maintaining an accurate geometry, allowing for greater flexibility in the artistic process. We demonstrate superior performance to an existing approach for surfacing ribbon sketches in this sparse setting.
|
Links
BibTeX
@article{scrivener2025faraday,
author = {Scrivener, Daniel and Cui, Daniel and Coldren, Ellis and Abulnaga, S. Mazdak and Bessmeltsev, Mikhail and Chien, Edward},
title = {Faraday Cage Estimation of Normals for Point Clouds and Ribbon Sketches},
year = {2025},
issue_date = {August 2025},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
volume = {44},
number = {4},
issn = {0730-0301},
doi = {10.1145/3731212},
journal = {ACM Trans. Graph.},
articleno = {49},
numpages = {13},
}
|